Utilizing 3D technology in higher education can promote experiential learning, deepen comprehension, and foster engagement among students. Instructors seeking to enrich their teaching methods have a powerful tool at their fingertips: their smartphones and cameras. With the aid of software applications like Qlone and Metashape, educators can use these devices to easily create their own 3D models. Qlone offers a mobile-friendly way to scan objects, while Metashape can process images from ordinary cameras to generate high-quality 3D models.
This article will introduce these two platforms, which educators are using to elevate their teaching out of two dimensions.
Qlone: 3D Scanning and AR features
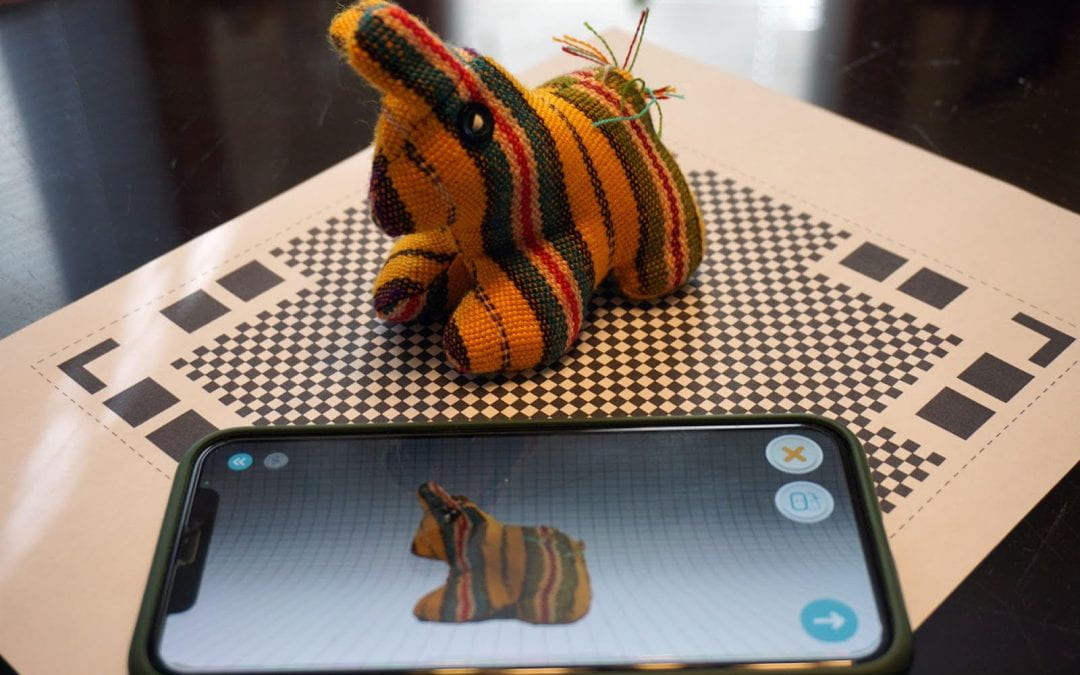
Qlone is a mobile application designed to scan real-life objects and transform them into high-quality 3D models. Qlone has integrated augmented reality (AR) functionality, allowing these models to be projected into real space directly through the app. With this app installed on your smartphone, you can convert a physical artifact into a 3D, rotatable model on a tablet or showcase a life-sized version in a lecture hall.
Scanning and Animating Objects Using Qlone

Employing Qlone in teaching is both innovative and intuitive. Start by placing an object on the Qlone mat which you can print directly from the app, then use the app to scan it from multiple angles. The app will then compile these images into a detailed 3D model. The AR feature can project this model onto any surface or overlay it in the real world for interactive exploration.
The animate feature of the Qlone app even allows you to add motion to your scanned objects. This dynamic capability enhances presentations and demonstrations, making digital replicas interactive.
Integration with Sketchfab and Other Platforms
In addition to its scanning capabilities, Qlone is also integrated with commonly used 3D platforms. You can directly upload your 3D models to platforms like Sketchfab for viewing and downloading, or Shapeways and i.materialise for 3D printing. With integration into Spatial, you can craft augmented reality experiences combining your 3D models and their 3D spaces.
Through these compatible platforms, you can create a holistic 3D ecosystem to provide your students with a more immersive and engaging learning experience.
Creative Teaching Options with Qlone
- Archaeology & Anthropology: Artifacts can be scanned and projected into the classroom, allowing students to observe and interact without the risk of damaging precious items. If you upload the models to Sketchfab, students worldwide can interactively explore and study them.
- Biology & Medicine: From plant specimens to anatomical models, Qlone provides students an immersive, 360-degree view. Visualize exploring a full-size 3D human heart during a lecture!
- Art & Design: Artists and designers can scan sculptures, prototypes, or other 3D artworks to create a digital portfolio. Additionally, they can study renowned pieces from every angle without geographical constraints.
- Engineering & Architecture: Prototype designs can be scanned and projected in real time and to scale, offering an immersive sense of space and structure.
- Astronomy: While not applicable for scanning celestial entities, Qlone can project models of planets, satellites, or other astronomical objects, making the mysteries of space more accessible.
Qlone serves as a bridge connecting the tangible and digital realms, presenting numerous possibilities for interactive university lectures and lessons.
Metashape: Make Photogrammetry Models with Ease
Metashape, formerly known as Agisoft PhotoScan, is a cutting-edge software solution used for photogrammetry — the art and science of extracting 3D information from photographs. The software processes images taken from various angles and stitches them together to generate highly detailed 3D models or orthographic images.
Creating 3D Models Using Metashape
Creating photogrammetry models using Metashape is a simple process, thanks to accessible tools like smartphones and digital cameras:
- Capture Photos: Firstly, choose the object you want to model and place it in a well-lit environment. Use your smartphone or camera to take multiple photos of the object from various angles. Make sure to capture every detail, as this will contribute to the accuracy of the final 3D model.
- Import Photos into Metashape: Transfer the photos to your computer and launch Metashape. Create a new project and import the captured photos by navigating to “Workflow” and selecting “Add Photos.”
- Align Photos: After importing, align the photos by going to “Workflow” and then “Align Photos.” The software will match common points in the images to begin constructing the 3D model. This process may take some time, depending on the number of photos and your computer’s processing power.
- Build the Mesh: Once the photos are aligned, you’ll have a sparse point cloud. To create a solid 3D model, go to “Workflow” again and select “Build Mesh.”
- Texturing: To add texture and color to your model, go to “Workflow” and choose “Build Texture.”
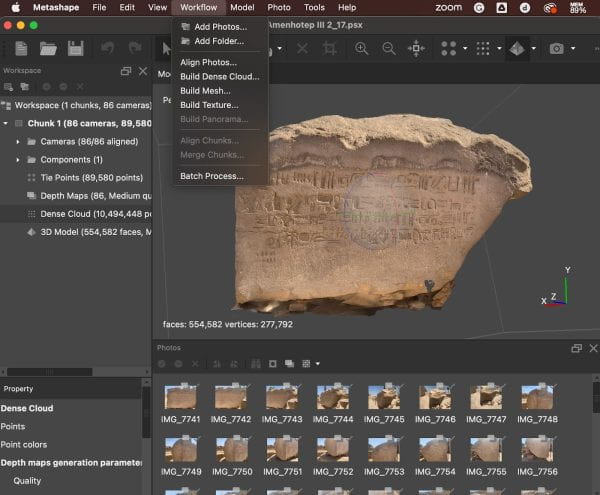
Once completed, you can export your 3D model in various formats for use in your teaching materials, presentations, or virtual environments. The cost of a Metashape educational license can vary, but could serve as a worthwhile investment to enhance student experience in the classroom.
Ways to Utilize Metashape in Higher Education
- Geography and Earth Sciences: Instructors can utilize Metashape to create detailed topographical maps from aerial photographs. This allows students to interact with 3D terrain models of geographical features, erosion patterns, and watershed dynamics, bringing them a step closer to fieldwork without leaving the classroom.
- Archaeology and Anthropology: When onsite excavations are challenging or impossible, photos from previous digs or current sites can be transformed into 3D replicas of archaeological finds or entire excavation sites.
- Biology and Medicine: For anatomy lessons, instead of relying solely on physical dissections or static models, educators can process high-resolution images of organs or biological specimens through Metashape. 3D models can be zoomed, rotated, and dissected virtually, offering a multi-dimensional view of complex biological structures.
- Art and Design: Art history or design students can delve deep into the intricacies of sculptures, paintings, or architectural marvels.
3D technology offers an avenue for educators to move beyond traditional lecture-based formats, encouraging active participation and real-world application of knowledge. It not only enriches the educational experience but also equips students with practical skills that are increasingly relevant in our technology-driven world.
Cover Image and First Image Credit: Joe Olivier
Further Resources
- Academic Technology Solutions Teaching Tools list
- Contacting ATS and ATS Virtual Office Hours (M-F)
- Weston Game Lab (WGL), a part of the Media, Arts, & Design Center at UChicago
- Qlone FAQs and Metashape FAQs and tutorials
- Data Visualization Laboratory